Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing is a manufacturing process through which material is deposited layer by layer consecutively producing customized geometric shapes.
This technology makes it possible to convert digital models into solid three-dimensional objects, without the need for molds or tooling of any kind, using 3D printing.
Process:
1. The part is designed in a CAD software.
2. The CAD model of the part is exported to an STL file.
3. This file is transformed and sent to the machine, where the material is deposited layer by layer successively forming the object.
With 3D printing applications, all industries can benefit from its advantages for their proof-of-concept, prototyping, production, or tooling processes.
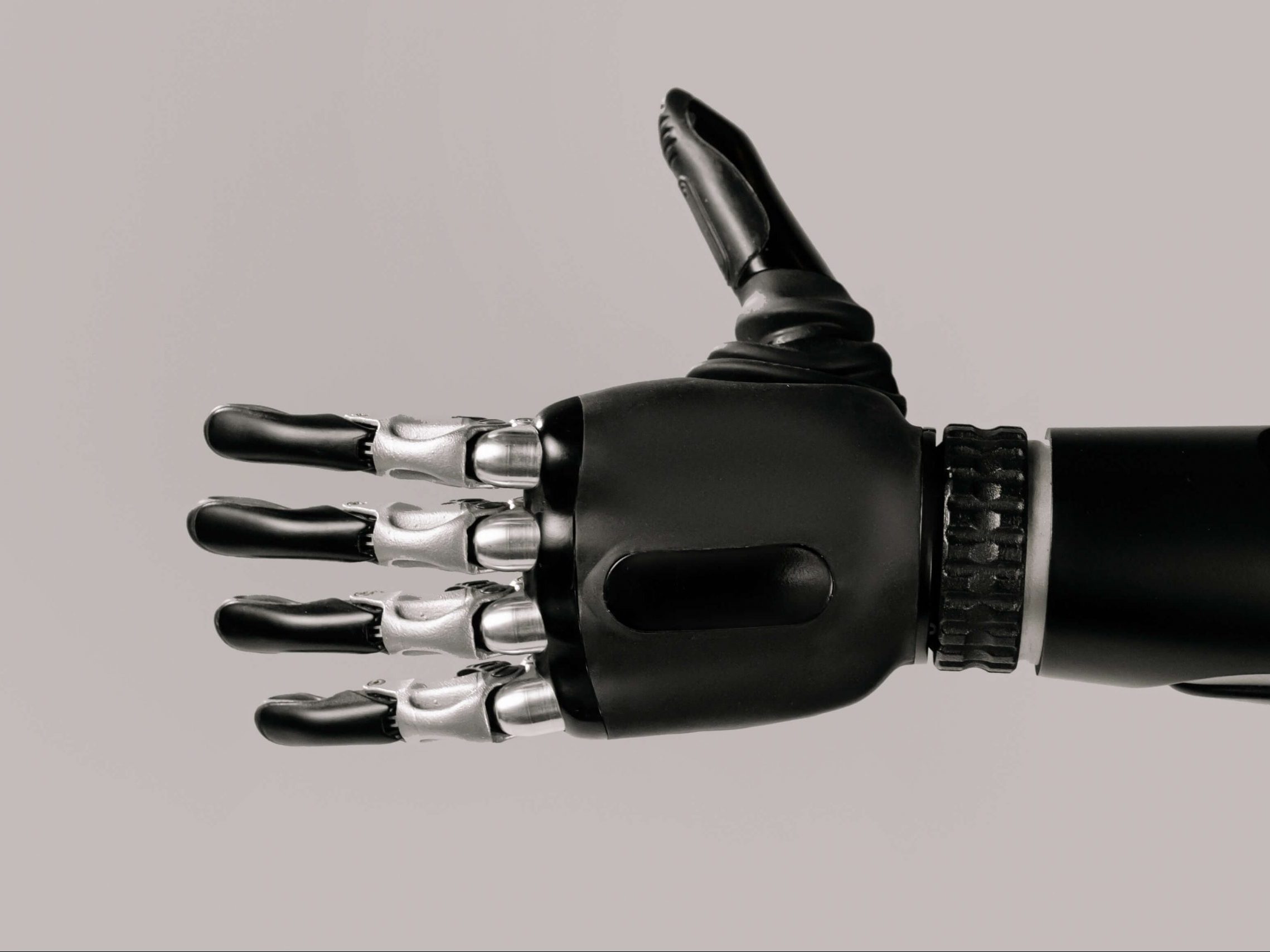


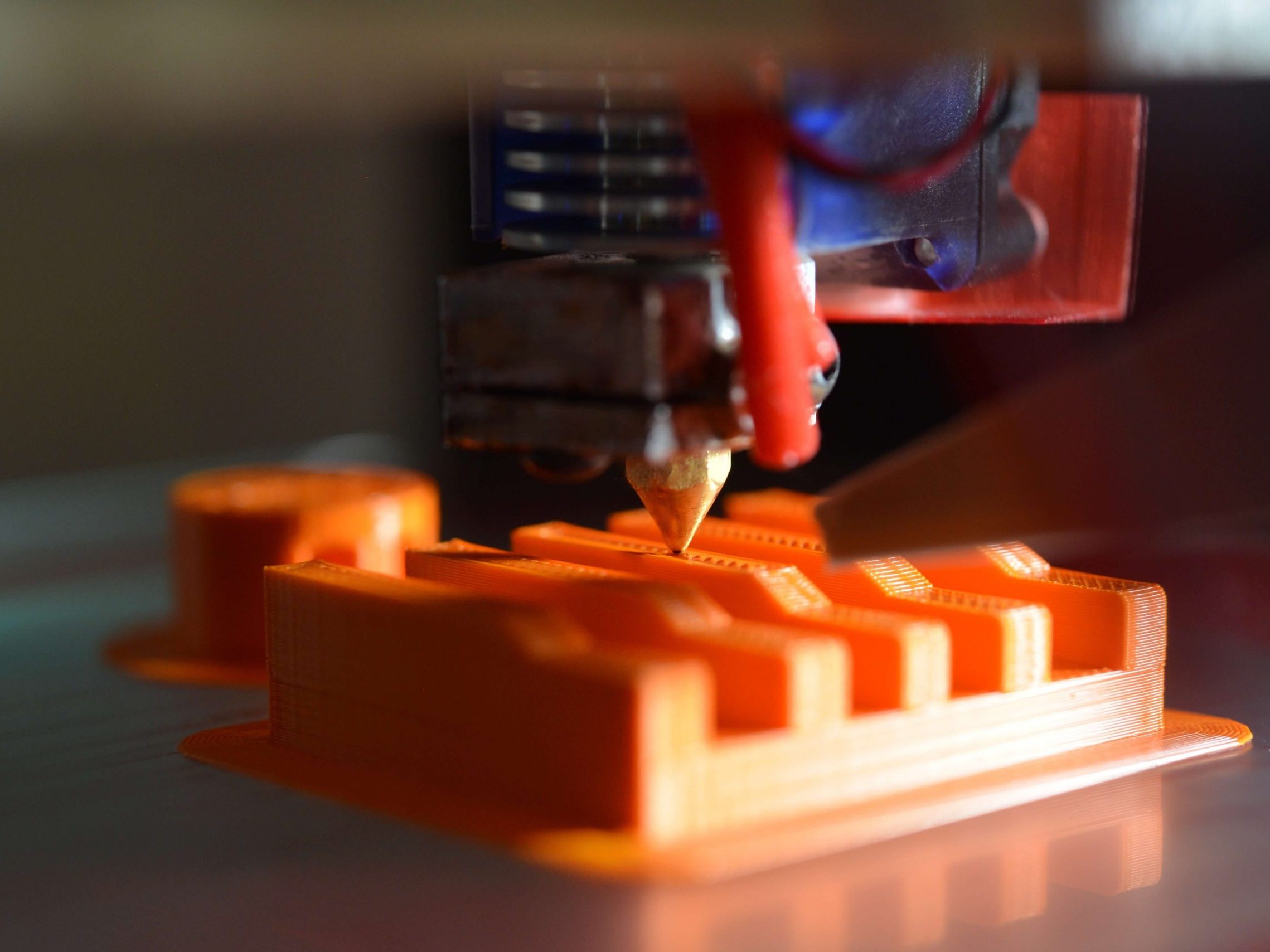









Soft jaws, end-use parts, and production forming tools.
Industrial tools, accessories, and work supports.
Actuators, crash test dummies, mechanical stops.
Welding accessories, thermoforms, thermosetting molds, injection mold inserts, blow molds.
Images belong to markforged.com





DESIGN
CAD design of the part.
OPTIMIZATION
Stress, load, and geometrical analysis of the part
PRODUCTION
3D printing with materials according to the technical specifications of the parts
CHECK
Review of the mechanical and chemical properties of the parts
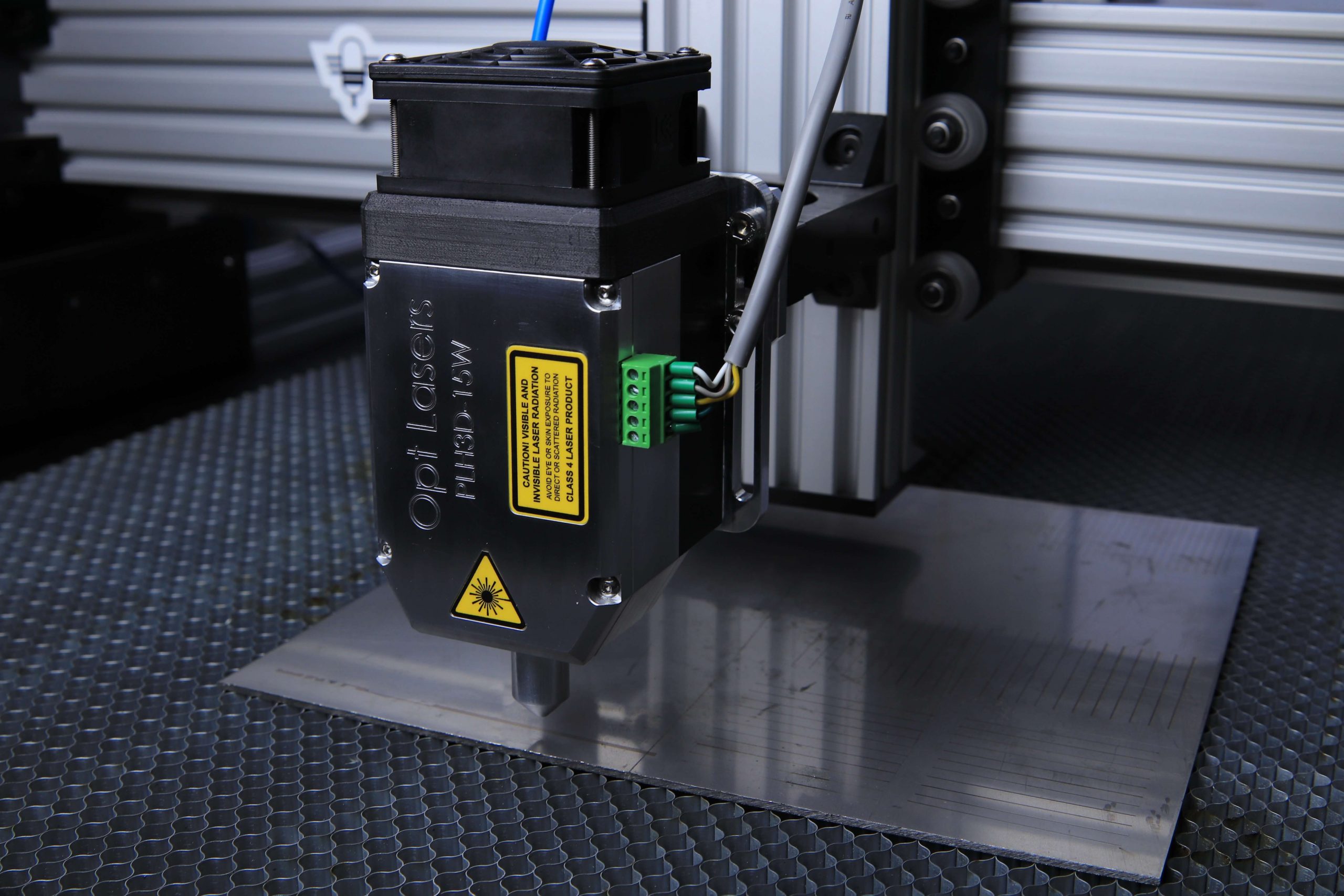
Plan and manage additive manufacturing operations.
Identify industrial needs.
Support companies in their development
Analyze the requirements of the part according to the application.
Design parts and generate CAD models.
Establish materials according to the application of the part.
Specify materials, costs, and duration of fabrication.
Andreas Gebhardt, Understanding Additive Manufacturing